Faces
Faces exist in planar topology only and represent the interior of an area formed by enclosing edges. A polygon is represented by one or more faces.
The edges describe the outer and inner boundaries of the face geometry and any edges contained by, but not bounding, the face.
To ensure that faces never overlap, 1Integrate will automatically insert a node and split into multiple edges wherever lines or polygon boundaries cross or meet. The features are not spit, but the underlying topology will be represented using multiple edges.
Adjacent faces share an edge, which means that the automatically maintained face-to-edge relationship can be used to very rapidly calculate geometric adjacency using Reference conditions.
Example: In the example diagram below, f0 is a universe face (sys:is_universe_face) that surrounds all other faces. When creating Rules and Actions the universe face is often ignored.
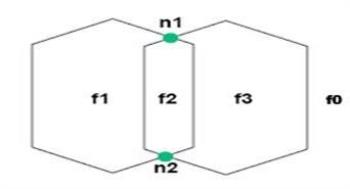
A face class has the following references:
|
Reference |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A |
|
|
A |
|
|
Faces can also use |