Non-Spatial Filtering
In addition to restricting the data load based on geometric filtering, you can restrict data load based on non-spatial expressions.
Non-spatial filtering can be applied to Open Data Task, Check Rules Task, Apply Actions Task, and Apply Action Maps Task. A Non Spatial Filter is configured on each of the task types, with the filter either selected from a number of default options, or having to be entered manually.
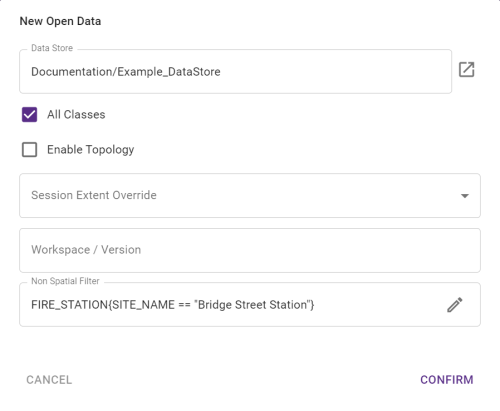
Note: Non-Spatial filters work much like a SQL WHERE clause, though is syntactically different.
Brackets "()" can be used to group expressions together to control the order of operations (BODMAS).
Example: ID == 1 + 2 * 3 will check that the ID is equal to 7, while ID == (1 + 2) * 3 will check that the ID is equal to 9.
Class Filters and Filter Syntax can be found in the tables below along with examples.
Note: Class and Attribute names are case sensitive when using a Non-Spatial filter.
Class Filters
Note: Class filters are optional and if omitted the filters will run on all classes.
By default, filters run on all classes. However, if your attributes are not the same across classes, this may cause the filter to fail to apply.
You may want to only filter specific classes, and load all the data from all other classes.
Example: CLASS1|CLASS2|CLASS3{filter} will apply the 'filter' to only the classes CLASS1, CLASS2, and CLASS3.
You can also filter everything out except for the specified classes.
Example: !CLASS1{filter} will apply the 'filter' to all classes except CLASS1.
Multiple class filters can be applied at once by separating them with commas.
Example: CLASS1{filter1},CLASS2|CLASS3{filter2},filter3, this will apply 'filter1' to CLASS1, 'filter2' to CLASS2, and CLASS3, and 'filter3' to all classes (including CLASS1, CLASS2, and CLASS3).
Note: Any classes not covered by the filters will be loaded as though there was no filter.
Filter Syntax
The following tables contain the syntax that can be used to create the non-spatial filters.
Constant Values
|
Constant Values |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Numbers |
Whole numbers and decimals. |
1 1.4 0.12 |
|
Strings |
Both ' and " can be used to denote strings so you can include the other character in the string itself. e.g. if you want to use " in the string, open the string with ': '"Example"'. |
'Text' "Text" "Text that has 'quotes'" |
|
Boolean Values |
True/False. |
true false |
|
Null |
No value. |
null |
Variables
|
Variable Values |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Attribute Names |
The name of the attribute in an object. If the source Data Store is case sensitive (e.g. a database) then this is also case sensitive. |
Check that the value of the
Check that the |
|
Session Parameter Values |
Session Parameter Values can be referenced by using the Value name, prefixed with a Note: Spaces in the name of the Session Parameter reference will need to be converted to underscores in the filter. It is also case sensitive. For more on Session Parameter Values, see Values. |
Check that the |
Operators
|
Supported Operator |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Boolean Operators |
||
|
&& |
This is an AND operator. |
Check that the ID attribute is greater than 5 and less than 10. |
|
|| |
This is an OR operator. |
Check that the |
|
! |
This is a NOT operator and negates the proceeding expression. |
Check that the |
|
String Operators |
||
|
== |
Equals to operator. |
Check that the |
|
!= |
Not equal to operator. |
Check that the |
|
+ |
Concatenate two strings. |
Check that the
Check that the |
|
Numeric Operators |
||
|
>= |
Greater than or equal to operator. |
Check that the |
|
<= |
Less than or equal to. |
Check that the |
|
> |
Greater than operator. |
Check that the |
|
< |
Less than operator. |
Check that the |
|
== |
Equal to operator. |
Check that the |
|
!= |
Not equal to operator. |
Check that the |
|
+ |
Add two numerical values. |
Check that the |
|
- |
Subtract two numerical values. |
Check that the |
|
^ |
To the power of. Use numerical values with this operator to multiply the value by itself. |
Check that the |
|
% |
Modulo operator. |
Check that the |
|
* |
Multiplication operator. |
Check that the |
|
/ |
Division operator. |
Check that the |
Functions
|
Function |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Numeric Functions |
||
|
min(x, y) |
Return the minimum of 2 numbers. |
Check that the |
|
max(x, y) |
Return the maximum of 2 numbers. |
Check that the |
|
round(x) |
Return the number rounded to the nearest whole integer. |
Check that the |
|
floor(x) |
Return the floor of the number (nearest whole integer, rounded down). |
Check that the |
|
ceil(x) |
Return the ceiling of the of the number (nearest whole integer, rounded down). |
Check that the |
|
clamp(x, y, z) |
Return first number clamped between second and third number. |
Check that the |
|
String Functions |
||
|
contains(string1, string2) |
Return true if first string contains the second. |
Check that the |
|
remove(string1, string2) |
Return first string with the second string removed from it. |
Check that the |
|
replace(string1, string2, string3) |
Return first string with all instances of second string replaced with third string. |
Check that the |
|
Casting Functions |
||
|
date(string1, string2) |
Parses the first string as a date with the second string supplied representing the date format pattern 1Integrate should use to interpret the given date. For use in timestamp attribute comparisons. Note: Date formats are defined using Java date formats e.g: |
Check that the |
|
string(number) |
Convert the given number to a string. For use in string attribute comparisons. |
Check that the |
|
number(string) |
Convert the given string to a number. For use in numerical attribute comparisons. |
Check that the |