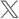Anatomy of Rules and Actions
Rules and Actions are made up of a series of nodes. Nodes display an expected component type for you to assign to it. Rules and Actions are only valid for use when all required nodes have been assigned a component. See Nodes in Detail for further information on nodes.
Components you select determine which nodes are added to a Rule or Action and whether those nodes are optional or not.
Parent and Child Nodes
The root node ("Rule For"/"Action For") is displayed at the beginning, and can be considered the top-level parent node. All other nodes are either a Parent, a Child, or both.
Components
Components add logic to the nodes in a Rule or Action. The type of component necessary for a node is always displayed on an empty node.
Any component that requires Child nodes will have them added automatically.
Example: A Check That Predicate will create the following 3 nodes in the order Value > Relation > Value.
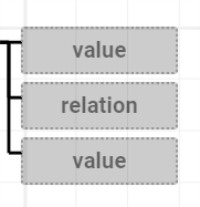
This will check the first Value against the second Value with a particular Relation such as equals or contains.
There are a few types of components and some of those have sub-types that are distinguished from the others because of their specialisations.
Component Types
|
Predicates are a high-level logical test that defines the syntax for both Rules and Actions. It defines the sequence in which tests are performed. |
|
|
Most Operations are Action Components. The Execute then Check Predicate is the exception, allowing all Operation types except for the Object and Report Operations. |
|
|
Relations compare two Values and return a result of true or false. |
|
|
Values are either a constant, a reference to objects, or a calculation that is used in a Predicate. |
Component Sub-Types
|
A built-in function is a Value for a Predicate node that returns a value calculated from one or more Values. |
|
|
A built-in operation is a Value for an Operation node that returns a value calculated from one or more Values. |
|
|
Aggregate functions can be added to a Values node to calculate a single result from one or more inputs, specified as the result of a Predicate. |