La fonction d’import CSV lance l’interface ci-dessous :
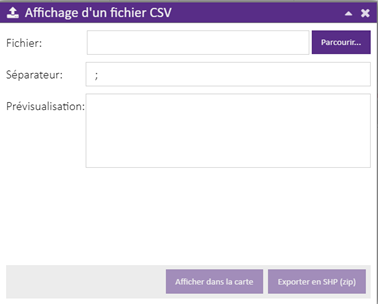
Figure 21 : Fonction « Import CSV »
Le fichier CSV doit contenir des données liées aux voies.
Le fichier doit avoir la structure suivante :
|
Nom
du champ |
Obligatoire |
Respect
du nommage |
|
Gestionnaire |
Oui |
Oui |
|
Voie |
Oui |
Oui |
|
Axe |
Oui |
Oui |
|
Plod |
Oui |
Oui |
|
Absd |
Oui |
Oui |
|
Plof |
Oui (pour les linéaires) |
Oui |
|
Absf |
Oui (pour les linéaires) |
Oui |
|
Champ attributaire 1 |
Non |
Non |
|
Champ attributaire 2 |
Non |
Non |
|
… |
|
|
Exemple de fichier :
|
Gestionnaire |
Voie |
Axe |
Plod |
Absd |
Plof |
Absf |
Arrachement |
Longueur |
Localisation |
|
CD |
D1 |
Principal |
1 |
13 |
1 |
17 |
Pelade,désenrobage
profond |
4 |
Sens axe V1 |
|
CD |
D1 |
Principal |
1 |
19 |
1 |
27 |
Pelade,désenrobage
profond |
8 |
Sens axe V1 |
|
CD |
D1 |
Principal |
2 |
62 |
2 |
87 |
Plumage,désenrobage
de surface |
12 |
Sens inverse V1 |
|
CD |
D1 |
Principal |
2 |
297 |
2 |
315 |
Plumage,
désenrobage de surface |
11 |
Sens axe V1 |
|
CD |
D1 |
Principal |
2 |
425 |
2 |
436 |
Plumage,
désenrobage de surface |
36 |
Sens axe V1 |
|
CD |
D1 |
Principal |
3 |
127 |
3 |
132 |
Plumage,
désenrobage de surface |
13 |
Sens inverse V1 |
Le délimiteur du fichier est « ; ».
La base de données contient 47918 voies.